Western Blotting Technique
Western blot (WB)—or immunoblot—is a workhorse immunoassay for most labs used to demonstrate antibody specificity, confirm gene expression, detect post-translational modifications (PTMs), diagnose diseases, and more. Specific detection of bands corresponding to the protein of interest result from successively probing your blot with primary and conjugated secondary antibodies. It is a widely used method for detection of a specific protein in a complex matrix, such as cell or tissue lysate (i.e. protein extracts).
The Western blot assay uses gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE or native PAGE) to separate proteins according to molecular weight. The proteins are then transferred from the gel onto a membrane (typically nitrocellulose or PVDF), which is then blocked with a protein blocking buffer to prevent non-specific binding and probed using a primary antibody to detect the protein of interest. This is followed by an incubation with a secondary antibody conjugated to a reporter molecule, allowing the visualization of the target protein; however, primary antibodies conjugated to a reporter do not require secondary antibody usage. Wash steps using a mild detergent that contains buffer are also typically performed after antibody incubations to remove any non-specific binding.
Western blot experiments can be performed in several formats, most of which require a conjugated secondary antibody to act as the reporter molecule. Reporter molecules include horseradish peroxidase alkaline phosphatase enzymes, and fluorophores. When reporter enzymes are used, chromogenic, or luminescent substrates can be applied for detection.
Fluorophore reporter molecules do not require substrate but they do require specialized equipment for data collection. Fluorescent detection is suitable for multiplex WB experiments where multiple targets can be detected in the same assay using fluorophore conjugates with non-overlapping emission spectra. Fluorescent WB is also ideal for quantitative analysis since detection allows for wide dynamic ranges and signal normalization.
The choice of WB membrane depends on the type of experiment to be performed. Most common membranes used are nitrocellulose or polyvinyldifluoride (PVDF). Nitrocellulose is easy to use and provides suitable data for most common enzymatic reporter experiments. Low fluorescent PVDF membranes are recommended for fluorescent Western blot applications.
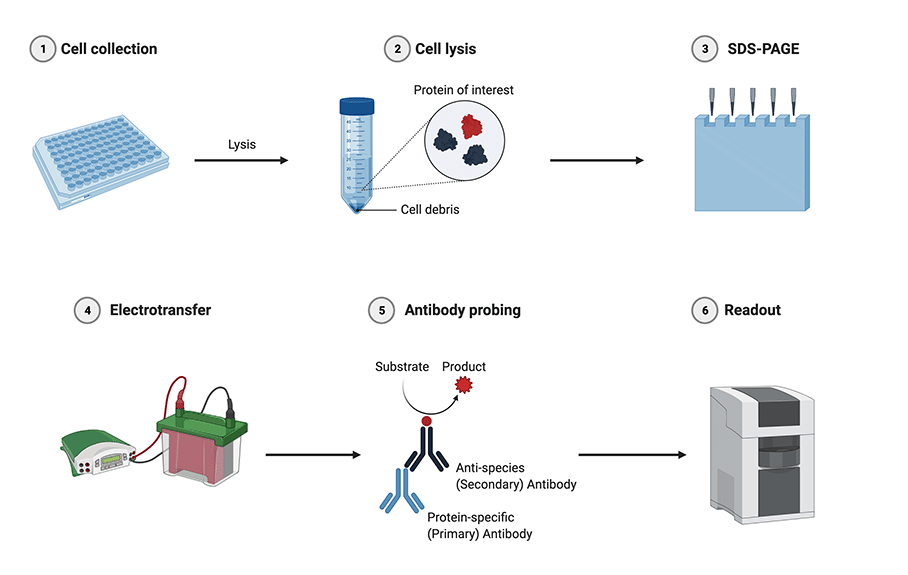
Figure: Western blotting procedure. 1. Cells expressing the protein of interest are collected; 2. Cells are lysed and centrifuged to prepare a protein suspension; 3. Proteins are separated by molecular weight using SDS-PAGE; 4. Proteins are transferred to a membrane using electrotransfer; 5. The membrane is incubated with a primary antibody specific for the protein of interest, this is followed by a secondary antibody conjugated to a reporter molecule; 6. The reporter molecule is visualized and photographed. (Created using BioRender.com)
Multi-lysate WB
As application-specific guidelines and standards for validating research antibodies increasingly becomes a subject of scrutiny by the scientific community, multiple approaches can—and should—be implemented to demonstrate the specificity of a primary antibody with adequate robustness. One such approach is the confirmation of target-specific antibody properties by the inclusion of cell lysates or cell lines known to contain or not the target of interest based on genomic and proteomic studies. The appropriate negative controls for cells naturally producing the target are the same cells in which the abundance of the target is selectively altered by chemically stimulation or genetic approaches.
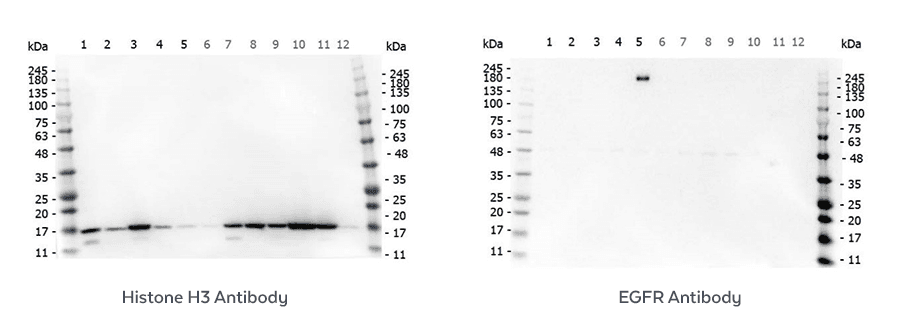
Rockland routinely scrutinize the specificity or its primary antibodies by assessing their performance in multi-lysate Western blots. A variety of conditions are evaluated for each target so that specificity, sensitivity and reproducibility can be determined. This ensures reliable performance and confirm lot-to-lot consistency.
Immunoprecipitation-WB
Immunoprecipitation (IP) is one of the most widely used approaches for antigen purification and detection. The approach uses antigen-specific antibodies to isolate an antigen of interest from a complex protein mixture that is subsequently analyzed by Western blotting in order to assess the relative amount and size of the target antigen itself and/or target-associated proteins.
Analysis of immunoprecipitated proteins by immunoblotting can be complicated because the reagent used to detect the WB staining antibody will often bind to the heavy and light chains of the precipitating antibodies. As described below, this problem can be easily corrected by using our TrueBlot® products that selectively bind staining antibodies only through increased sensitivity, less background noise, and enhanced accuracy.
IP Western blots provide highly specific results, yet often suffer from heavy/light chain blotting, contamination, and ongoing interference. TrueBlot® products solve nearly all of these problems through increased sensitivity, less background noise, and enhanced accuracy. TrueBlot® reagents enable you to generate clear, best-quality data in your Immunoprecipitation and Western blot protocols. Available in several options, from TrueBlot® IP beads, TrueBlot® secondary antibodies, to complete IP/Western blot kits from goat, mouse, or rabbit.
In-Cell Western
In-cell western (ICW) assays—or cell based assays, cell-based ELISA, In-Cell ELISA (ICE), or Fast Activated Cell-based ELISA (FACE)—allow researchers a simple and rapid assay method for the quantification biomarkers and signaling proteins in whole cells using antibodies. The Odyssey® infrared imaging system by LICOR® is well suited for ICW; however, other imaging systems may also be used. The method combines the specificity of a WB with the quantification of an ELISA. ICW assays can be used for detection of proteins in fixed cells or proteins with physiological- or biologically-relevant cellular context and in multiplex quantification of two targets using 700 nm and 800 nm channels with appropriate dye-conjugated antibodies.
Many of Rockland's antibodies have been validated for use in ICW and because ICW assays are related to immunofluorescence (IF), most antibodies that have been validated and approved for IF can be similarly used with ICW assays as well.
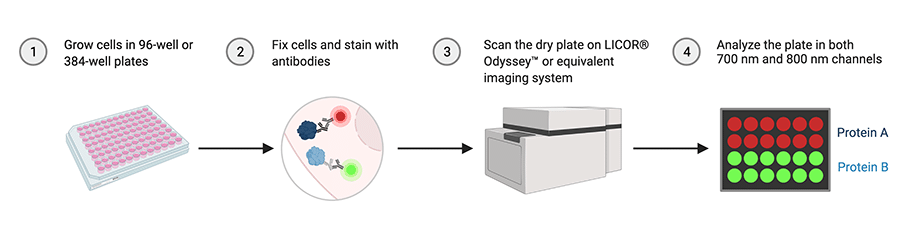
Figure: In-cell western technique allows multiplex antibody-based quantification of two target proteins using 700 nm and 800 nm channels in fixed cells. (Created using BioRender.com)
Secondary Antibodies for WB
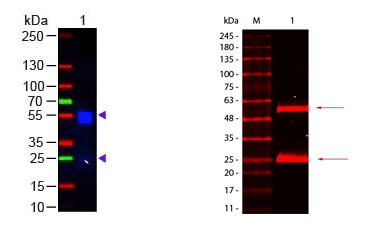
Secondary antibody conjugates are ideal for Western blotting. When choosing a secondary antibody conjugate for an antibody assay consideration must be given to target species, conjugate (i.e. peroxidase, FITC, Biotin) and host species. In addition to standard secondary antibodies, Rockland offers pre-adsorbed secondary antibodies which are suitable for detection methods where cross-reactivity may be an issue.
Reporter enzymes are used extensively in molecular biology because they allow visualization or detection of immune complexes. Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) is a widely used reporter enzyme, and depending on the substrate it can yield a chromogenic, or luminescent product (chemiluminescence). Alkaline phosphatase is also used, most typically as the reporter in chromogenic Western blot assay format.
Antibodies Conjugated to Alkaline Phosphatase (AP) are used in the detection of proteins in Western blotting and ELISA immunoassay procedures. The alkaline phosphatase (AP) catalyzes colorimetric reactions using BCIP/NBT substrates. Secondary Antibody conjugates are conjugated to the highest grade of alkaline phosphatase using Rockland’s proprietary technology.
Rockland conjugates a broad group of secondary antibodies to many of the classic and next generation of fluorescent markers including fluorescein, Texas Red, Phycoerythrin. Rockland also produces many next generation flurochrome dyes. These are designed for detection of primary antibodies in multiplex, multi-color analysis. Next generation fluorochrome conjugates (Atto-tec dyes, DyLight™ dyes) offer superior absorption (high extinction coefficient), high fluorescence quantum yield and superior high photostability. All of the conjugates are ideal for various immunofluorescence based assays including fluorescent Western blotting, immunofluorescence microscopy, FLISA, and more.
Substrates for WB
Chromogenic Substrates
Chromogenic substrates are used in colorimetric assays since they result in a measurable color change in the presence of an enzyme-antibody complex bound to specific analytes. For WB using horseradish peroxidase (HRP) in colorimetric detection TMB and DAB substrates are commonly used. Alkaline phosphatase (AP) chromogenic substrates include BCIP/NBT, which usually exhibit the highest sensitivity and reliable detection of AP activity. Chromogenic blotting substrates are available from Rockland in a variety of specifications and formats. The appropriate substrate choice depends on the enzyme label, desired sensitivity and form of signal or method of detection needed.
The peroxidase reaction with our TMBM substrate produces a water-soluble blue product that can be precipitated onto a membrane. The precipitating product produces blue to dark blue bands in the enzyme location. TMBM is well suited to applications that require high signal-to-noise. DAB is another peroxidase substrate and yields a brown precipitate in the presence of HRP and peroxide.
The NBT/BCIP reagent is also commonly used in chromogenic Western blot immunoassays. NBT serves as an oxidant and BCIP as the alkaline phosphatase substrate. Together NBT and BCIP form reactants in the presence of alkaline phosphatase which yields a dark purple to black, water-insoluble, precipitant product providing strong sensitivity.
Chemiluminescent Substrates
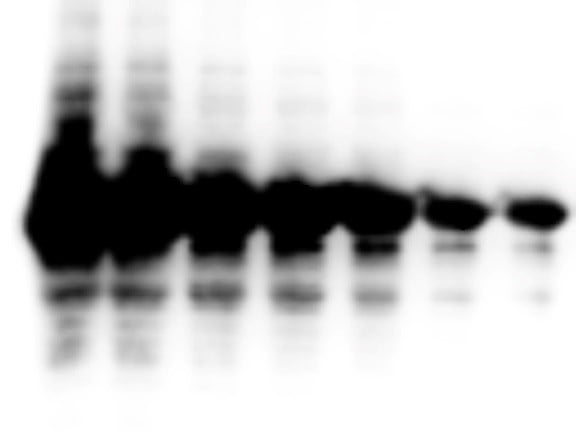
Rockland produces several luminol based substrates with chemiluminescence for the detection of horseradish peroxidase (HRP). The FemtoMax™ Super Sensitive HRP Substrate is designed for high performance in Western blotting and is functional on both nitrocellulose and PVDF membranes. FemtoMax™ produces chemiluminescence and allows for the detection of down to femtogram (10-15) amounts of antigen. Detection methods may include photographic film or other imaging methods, including highly sensitive CCD camera based systems.
Chemiluminescent substrates offer several advantages over the chromogenic substrates. Mainly, these systems are significantly more sensitive for detection of enzymatic activity without the use of radioactive isotopes, luminescent detection typically happens within few minutes and the signal is more amenable to quantification because it requires the use of digital charge-coupled devices (CCD) for detection that allow for a wide dynamic range using prolonged exposure.
Blocking Buffers for WB
When performing a Western blot, the blocking buffer should not be overlooked. The blocking buffer fills in the locations on the membrane that can bind protein and cause background if not treated. The critical reagent in a blocking buffer is protein, where the protein is non-antibody reactive. Popular blocking proteins include non-fat dried milk (NFDM), BSA, casein, and combinations thereof. Of note, a single blocking agent may not be sufficient for all Western applications. Some blocking agents can interfere with primary antibody activity, may be incompatible with the reporter system in use, or produce undesired auto-fluorescence. We develop several blocking buffer reagents suitable for all Western blot applications, including Blotto and BSA for standard applications, and a specially formulated Blocking Buffer for Fluorescent Western Blotting.
Fluorescent blocking buffers are specially formulated to preserve the fluorescence from fluorochrome-dye conjugated secondary antibodies and also provide an ultra-low background compared to other blocking buffers. Our buffers work with many fluorescent secondary antibody conjugates including, FITC, IRDye®, Atto dye, and DyLight™ dye. Our blocking buffer for fluorescent Western blotting is exceptionally good in standard chemiluminescent blotting applications and is demonstrated to be superior for 2D WB experiments in head-to-head comparisons with other blocking reagents.
Kits for WB
Western blot kits may be available for your assay, simplifying your reagent needs. We offer kits for chemiluminescence, fluorescent, and chromogenic immunoassay formats. Our kits are configured with simple and easy-to-use protocols for both beginner and expert users alike. Kits are species-specific for detection of mouse or rabbit primary antibodies and come ready as a format-specific package, including a membrane blocking reagent, washing buffers, secondary antibodies, and substrate (if required). Some of our more popular kits include FentoMax™ kits for chemiluminescent applications (human, mouse, rabbit, goat), and Dylight™ kits for detection on fluorescent Western blot protocol imaging systems.